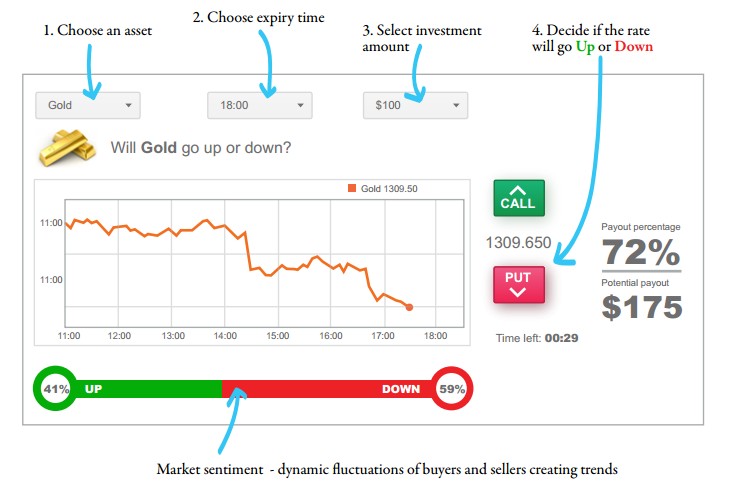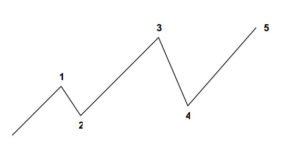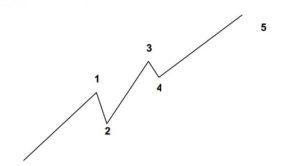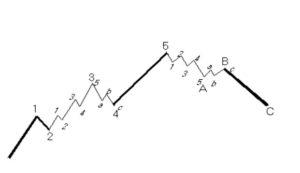
Trend reversal patterns are essential indicators of the trend end and the start of a new
movement. They are formed after the price level has reached its maximum value in the
current trend. The main feature of trend reversal patterns is that they provide information
both on the possible change in the trend and the probable value of price movement.
These patterns serve to indicate to binary options traders, that the ongoing trend is about to change the course. A pattern formed during an uptrend signals a trend reversal where the price will head down soon. On the other hand a reversal chart formed during a downtrend indicates that the price will move up.
One of the key factors to recognize a chart pattern is to know where certain patterns are
most likely to occur in the prevailing trend. Patterns occurring at market tops are known
as distribution pattern, where Binary Options traders more enthusiastically sell than buy the trading instrument. Conversely, patterns occurring at market bottoms are known as accumulation patterns, where traders more actively buy than sell the trading instrument.

Head and Shoulders:
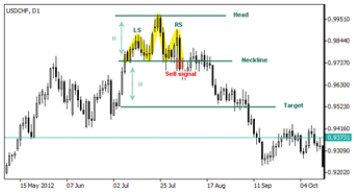
Head and shoulders indicate both the end of trend and the possible change in the direction of asset’s price. The given pattern is formed in an uptrend representing three peaks of the market price arranged at different levels. Two lower peaks called shoulders are located at two sides of the highest peak called the head.
The pattern’s lows are connected by support level called a neckline. If the price falls below the neckline or support level a sell signal arises. Though prices may rebound to the neckline forming a resistance level it is expected that the decline will continue.
Inverse Head and Shoulders:
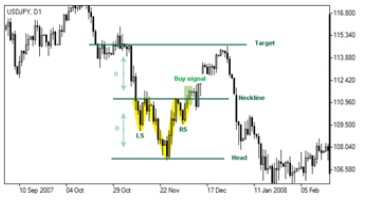
Inverse head and shoulders represent a trend reversal pattern indicating the change in direction of the asset’s price. Being formed in a downtrend this pattern comprises three consecutive lows of the market price which are arranged at different levels: two
higher bottoms called shoulders are located at two sides of the lowest bottom called head.
The pattern’s highs are connected by resistance level called a neckline. If the price climbs above the neckline or resistance level a buy signal arises. Though prices may rebound to the neckline forming a support level it is expected that the surging will continue.
Double Top:
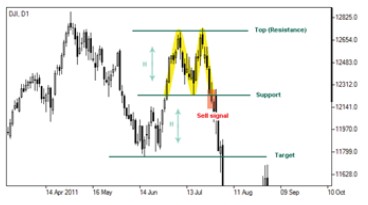
Double top represents a trend reversal pattern which precedes existing trend reversal. Though it is formed in an uptrend there is an expectation that it may be followed by a drop in prices. Moreover, if it takes much time for the pattern to be formed more reliable it will be. This pattern comprises two horizontal lines (support and resistance levels) connecting two most recent highs and a low of the price. When the market price breaks the pattern’s low or support level the formation is considered completed. In such a case it identifies downward direction of the trend serving as a signal to sell.
Double Bottom:
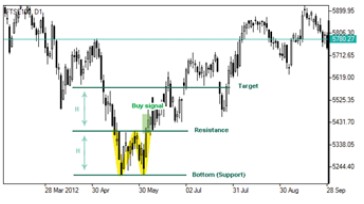
Double bottom represents a trend pattern which serves as an existing downtrend reversal.
Though it is formed in a downtrend there is an expectation that it may be followed by a rally in prices. Moreover, if it takes much time for the pattern to be formed more reliable it will be. This pattern comprises two horizontal lines (support and resistance levels) connecting two most recent low and a high of the price. The two recent lows form a support level and the most recent local high is considered a resistance level.
The formation is considered to be completed when the market price breaks above the pattern’s maximum or resistance level. In such a case it identifies upward direction of the trend serving as a signal to buy.
Triple Top:
Triple top is a price pattern which is formed in an uptrend and is followed by a drop in prices. This pattern comprises three consecutive peaks arranged at the same level and two bottoms. The highs and lows of the price are connected by resistance and support lines.
The formation is considered to be completed if the price breaks the pattern’s minimum. It can be interpreted as a downward direction of the trend serving as a signal to sell.
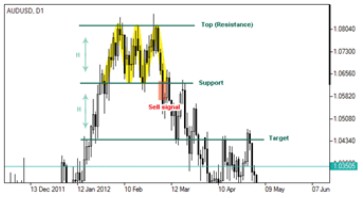
Triple Bottom:
Triple bottom is a price pattern which is formed in a downtrend and is followed by a rise in prices. This pattern comprises three consecutive lows arranged at the same level and two highs located between them. The lows and highs of the price are connected by support and resistance lines respectively. The formation is considered to be completed if
the price breaks the pattern’s maximum. It can be interpreted as an upward direction of the trend serving as a signal to buy.
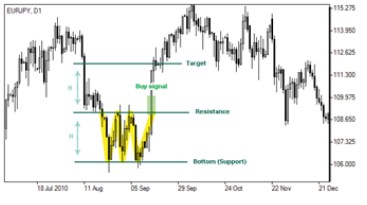
Forex Diamond:
Diamond is a trend pattern serving as a confirmation of the existing trend reversal. Generally it tends to appear in an uptrend. This pattern is formed of four limited trend lines which represent two support lines below and two resistance lines above. Those support and resistance lines connect recent lows and highs respectively thus forming a figure which visually resembles a brilliant or a rhomb. The formation can be thought to be completed when the support line at the right is violated. Therefore it can be interpreted as a downward direction of the trend serving as a signal to sell.
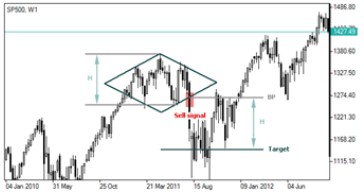
In conclusion, it would be important to note that a reversal pattern does not necessarily suggest a complete reversal in trend. It merely indicates a change or pause in direction. This can signify anything from a slowdown in trend, sideways trading after an established trend, or a full turnaround following a reversal candle pattern.