Forex brokers are financial intermediaries that provide traders with access to the foreign exchange market. Unlike stock exchanges where you can theoretically buy shares directly, the forex market operates as an over-the-counter marketplace with no centralized location. This decentralized nature means individual traders need a bridge to connect with market liquidity, and that’s exactly what forex brokers provide.
When you place a trade through a forex broker, they facilitate the transaction by either matching you with another trader who wants to take the opposite position or by taking the other side of the trade themselves. This process happens in milliseconds and allows you to buy and sell currency pairs with the click of a button, regardless of whether you’re trading from your home office or on the go with a mobile app.
The relationship between traders and brokers has evolved significantly over the past two decades. In the early days of retail forex trading, spreads were wide, platforms were clunky, and regulatory oversight was minimal. Today’s forex brokers operate in a highly competitive and regulated environment, offering tight spreads, sophisticated trading platforms, and comprehensive educational resources. This evolution has democratized forex trading, making it accessible to traders with accounts as small as $10, though such micro-accounts come with their own set of challenges and limitations.
Modern forex brokers also serve multiple roles beyond simple trade execution. They act as educators, providing market analysis, trading tutorials, and economic calendars. Many offer social trading features where you can copy the trades of successful traders, while others provide advanced charting tools and algorithmic trading capabilities. Understanding these varied services helps you appreciate why broker selection is so crucial to your trading success.
Types of Forex Brokers: Understanding the Business Models
The forex brokerage industry operates on several distinct business models, each with implications for how your trades are executed and how the broker generates revenue. Understanding these models is essential because they directly affect your trading costs, execution quality, and potential conflicts of interest.
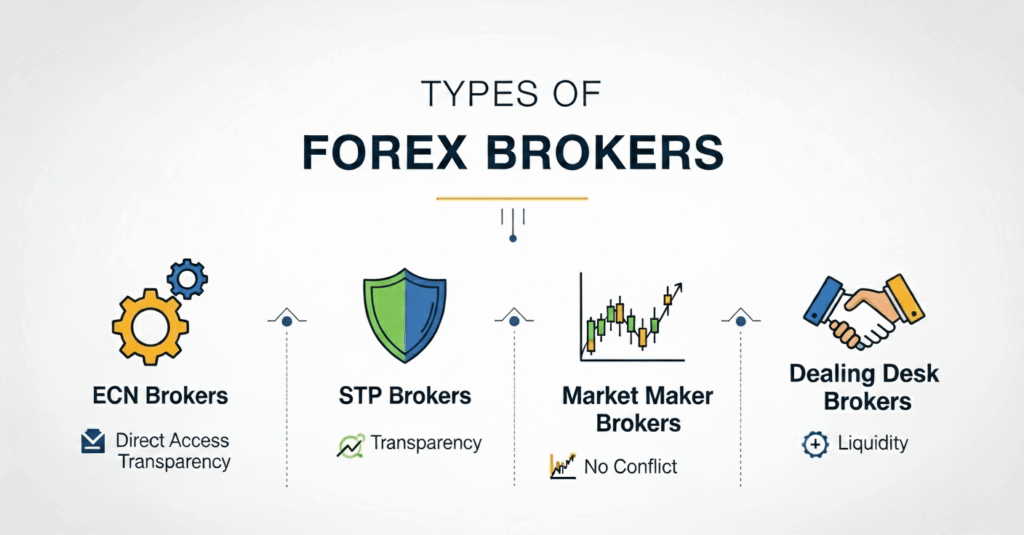
Market makers, also known as dealing desk brokers, create their own bid and ask prices for currency pairs. When you place a trade with a market maker, they take the opposite side of your position. If you buy EUR/USD, the broker sells it to you from their inventory. This model allows market makers to offer fixed spreads and guarantee trade execution, but it also creates a potential conflict of interest since your losses become their profits. However, reputable market makers manage this conflict through sophisticated risk management systems and by hedging large net positions with liquidity providers.
The advantage of trading with market makers becomes apparent during volatile market conditions. While other broker types might experience slippage or requoting, market makers typically honor their quoted prices regardless of market conditions. They also tend to offer more comprehensive educational resources and customer support since they benefit from having successful, long-term clients rather than traders who blow up their accounts quickly.
Electronic Communication Network brokers operate differently by connecting you directly with liquidity providers such as banks, hedge funds, and other financial institutions. ECN brokers don’t take the opposite side of your trades; instead, they match your orders with other market participants. This model eliminates conflicts of interest but typically involves commission charges on top of variable spreads. ECN brokers are often preferred by professional traders and scalpers who value direct market access and transparent pricing.
Straight Through Processing brokers represent a hybrid approach, routing your trades directly to liquidity providers without dealing desk intervention. STP brokers make money through spreads rather than commissions, but unlike market makers, they don’t take positions against their clients. Many modern brokers combine STP and ECN features, offering different account types to cater to various trading styles and experience levels.
Key Features That Define Quality Forex Brokers
When evaluating forex brokers, trading costs often receive the most attention, and rightfully so. The difference between a broker charging 1.5 pip spreads and another charging 0.8 pips can amount to thousands of dollars over the course of a year for active traders. However, focusing solely on advertised spreads can be misleading. Some brokers offer extremely tight spreads during quiet market hours but widen them significantly during news events or volatile periods.

Commission structures vary widely across different broker types and account levels. ECN brokers typically charge commissions ranging from $3 to $7 per standard lot, while STP and market maker brokers usually build their profits into the spread. When comparing costs, calculate the total cost of trading by adding spreads and commissions together. A broker advertising zero commissions might have wider spreads that result in higher overall trading costs than a commission-based broker with tighter spreads.
Trading platforms serve as your primary interface with the forex market, making their quality and reliability crucial to your success. MetaTrader 4 remains the most popular platform globally, offering robust charting capabilities, automated trading through Expert Advisors, and a vast marketplace of indicators and tools. MetaTrader 5 provides additional features including more timeframes, economic calendar integration, and improved backtesting capabilities.
Many brokers also offer proprietary platforms designed to differentiate their services. These platforms often feature unique tools, better integration with broker services, and enhanced user interfaces. However, proprietary platforms can create dependency issues if you ever want to switch brokers, since you’ll need to learn a new platform and potentially rebuild any automated trading systems.
The range of tradeable instruments has expanded dramatically in recent years. While currency pairs remain the core offering, most forex brokers now provide access to commodities, indices, individual stocks, and cryptocurrencies through Contracts for Difference. This diversification allows you to hedge forex positions or take advantage of opportunities in other markets without maintaining multiple brokerage accounts.
Leverage capabilities vary significantly between brokers and depend heavily on your location and regulatory environment. European brokers are limited to 30:1 leverage for major currency pairs due to ESMA regulations, while brokers in other jurisdictions might offer leverage up to 1000:1. Higher leverage amplifies both profits and losses, making risk management even more critical. Professional traders often prefer moderate leverage levels that allow for proper position sizing without excessive risk.
How to Choose the Right Forex Broker for Your Needs
Selecting the right forex broker requires honest self-assessment of your trading style, experience level, and financial situation. Scalpers who execute dozens of trades daily have dramatically different needs compared to swing traders who hold positions for days or weeks. High-frequency traders prioritize execution speed and low costs per trade, while longer-term traders might value comprehensive research tools and educational resources more highly.
Your account size significantly influences which brokers and account types are most suitable. Micro accounts with $100 deposits face limitations such as limited leverage, wider spreads, and restricted access to premium tools. However, they provide an excellent starting point for beginners to gain real trading experience without risking substantial capital. Standard accounts typically require larger deposits but offer better trading conditions and access to advanced features.
Regulatory compliance should be non-negotiable in your broker selection process. Regulated brokers must adhere to strict capital requirements, maintain segregated client accounts, and submit to regular audits. Major regulatory bodies include the Financial Conduct Authority in the UK, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission in the US, the Australian Securities and Investments Commission, and the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission in Europe.
The regulatory environment also affects available leverage, negative balance protection, and dispute resolution procedures. Brokers regulated in multiple jurisdictions often provide the highest level of protection, though they may also face more restrictions on the services they can offer. Always verify a broker’s regulatory status through official regulatory websites rather than relying on claims made on the broker’s own website.
Customer service quality becomes critically important when you encounter technical issues, have questions about your account, or need assistance with withdrawals. Test a broker’s customer service before opening an account by asking detailed questions about their services, trading conditions, and policies. Response times, knowledge levels, and available communication channels vary dramatically between brokers.
Platform stability and reliability are often overlooked until you experience problems during important trading opportunities. Server downtime during major news events or volatile market conditions can result in missed opportunities or inability to close positions. Research a broker’s technical infrastructure, backup systems, and historical uptime records. Many brokers offer multiple platform options or web-based alternatives to ensure continued access during technical difficulties.
Red Flags and Warning Signs to Avoid
The forex industry, despite increased regulation, still attracts unscrupulous operators who prey on inexperienced traders. Unrealistic promotional offers represent one of the most common red flags. Brokers offering 100% deposit bonuses, guaranteed profits, or risk-free trading are likely operating unsustainable business models or employing deceptive marketing practices.

Bonus offers, while attractive, often come with restrictive terms that make them difficult or impossible to withdraw. Common restrictions include minimum trading volume requirements, time limitations, and restrictions on trading strategies. Some brokers use bonuses to lock clients into their platform, making it difficult to withdraw funds without forfeiting the bonus and sometimes even the original deposit.
Unregulated brokers pose significant risks to your capital and should be avoided regardless of the trading conditions they offer. Without regulatory oversight, these brokers face no consequences for engaging in practices such as price manipulation, refusing withdrawals, or simply disappearing with client funds. The cost savings from lower spreads or reduced regulatory compliance never justify the risks associated with unregulated brokers.
Withdrawal difficulties represent another major warning sign. Legitimate brokers process withdrawal requests promptly and transparently, typically within one to three business days for electronic transfers. Brokers who delay withdrawals, impose excessive fees, or create bureaucratic obstacles are often experiencing financial difficulties or operating fraudulent schemes.
Poor execution quality can significantly impact your trading results even with regulated brokers. Consistent requoting, excessive slippage during normal market conditions, or platform freezes during volatile periods suggest inadequate infrastructure or deliberate manipulation. Monitor your trade execution quality carefully and document any suspicious patterns.
Getting Started: Opening and Managing Your Broker Account
The account opening process with reputable forex brokers has become increasingly streamlined while maintaining necessary security measures. Most brokers now offer fully digital onboarding that can be completed within 30 minutes, though full verification might take one to three business days depending on document review requirements.

Know Your Customer regulations require brokers to verify your identity, address, and financial situation before allowing you to trade. Typical documentation includes a government-issued photo ID, recent utility bill or bank statement for address verification, and sometimes proof of income for larger accounts. Having these documents readily available expedites the account opening process.
Demo accounts provide invaluable opportunities to test trading platforms, strategies, and broker services without risking real money. However, demo trading differs from live trading in important ways. Demo accounts typically offer better execution conditions, don’t reflect the psychological pressure of trading real money, and may not accurately represent spreads during volatile market conditions. Use demo accounts for platform familiarization and basic strategy testing, but transition to live trading with small positions to gain realistic experience.
Funding your trading account involves choosing between various deposit methods, each with different processing times, fees, and minimum amounts. Bank wire transfers typically offer the highest deposit limits but may take several business days to process and involve fees from both your bank and the broker. Credit and debit card deposits process quickly but often carry higher fees and lower limits. Electronic wallets like PayPal, Skrill, or Neteller provide good compromises between speed and cost for many traders.
Withdrawal procedures vary significantly between brokers and payment methods. Most regulated brokers require withdrawals to be sent back to the original funding source to comply with anti-money laundering regulations. This means if you deposited funds via credit card, your withdrawals must go back to that same card up to the original deposit amount, with any profits typically sent via bank transfer or electronic wallet.

Advanced Considerations for Serious Traders
Professional traders often require specialized services and trading conditions that aren’t necessary for casual traders. Prime brokerage accounts offer institutional-level spreads, direct market access, and dedicated account management but typically require substantial minimum deposits ranging from $25,000 to $100,000 or more. These accounts provide access to liquidity pools, advanced order types, and sometimes allow for custom leverage arrangements.

Algorithmic trading capabilities have become increasingly important as more traders seek to automate their strategies. MetaTrader platforms support Expert Advisors that can execute trades automatically based on predefined criteria. Some brokers also offer Virtual Private Server hosting to ensure your automated strategies continue running even when your personal computer is offline.
Social trading and copy trading platforms allow you to automatically replicate the trades of successful traders. While these services can provide valuable learning opportunities and potentially profitable results, they also involve additional risks. The performance of copied traders can change suddenly, and you have no control over the timing or risk management of copied trades. Always research the track record and trading style of any trader you consider copying.
Multi-asset trading capabilities enable you to diversify your portfolio beyond forex pairs. Many modern brokers offer CFDs on stocks, commodities, indices, and cryptocurrencies alongside traditional currency pairs. This diversification can provide hedging opportunities and allow you to capitalize on trends in different markets using a single trading account.
The Future of Forex Brokerage
Technological advancement continues reshaping the forex brokerage industry at an unprecedented pace. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being integrated into trading platforms to provide personalized insights, automated risk management, and enhanced market analysis. Some brokers now offer AI-powered trading assistants that can help identify potential trading opportunities and optimize position sizing based on your historical performance.

Mobile trading has evolved from basic functionality to comprehensive trading environments that rival desktop platforms. Modern mobile apps offer full charting capabilities, economic calendar integration, and even social trading features. The shift toward mobile-first design reflects changing trader preferences and the global nature of forex markets that require 24-hour accessibility.
Blockchain technology and cryptocurrency integration represent emerging trends that may significantly impact forex trading. Some brokers now accept cryptocurrency deposits and offer crypto-to-fiat trading pairs. Blockchain technology also promises to improve trade settlement, reduce counterparty risk, and enhance transparency in trade execution.
Regulatory evolution continues shaping the industry landscape. Recent years have seen increased focus on client protection through measures such as negative balance protection, standardized risk warnings, and restrictions on marketing to inexperienced traders. While these regulations may limit some services, they generally improve the safety and transparency of forex trading.
Conclusion
Choosing the right forex broker is one of the most important decisions you’ll make as a currency trader. The broker you select will influence every aspect of your trading experience, from the costs you pay to the platforms you use and the level of support you receive. While the abundance of options might seem overwhelming, understanding the key factors we’ve discussed will help you navigate this decision with confidence.
Remember that the “best” forex broker is highly individual and depends on your specific needs, trading style, and experience level. A broker that works perfectly for a scalping strategy might be entirely unsuitable for long-term position trading. Take time to honestly assess your requirements, test multiple brokers through demo accounts, and don’t rush into a decision based solely on promotional offers or flashy marketing.
The forex market offers tremendous opportunities for those who approach it with proper preparation and realistic expectations. Your choice of broker will either support your journey toward trading success or create unnecessary obstacles along the way. Invest the time needed to make an informed decision, and don’t hesitate to switch brokers if your current provider no longer meets your evolving needs.
Start your broker evaluation process today by opening demo accounts with two or three regulated brokers that meet your initial criteria. Test their platforms, analyze their costs for your typical trading patterns, and evaluate their customer service quality. Your future trading success may well depend on the foundation you build through careful broker selection.
Frequently Asked Questions About Forex Brokers
How do I know if a forex broker is legitimate and safe to use?
Verify that the broker holds valid licenses from recognized regulatory authorities such as the FCA (UK), CFTC (US), ASIC (Australia), or CySEC (Cyprus). Check their regulatory status on official government websites, not just their marketing materials. Legitimate brokers also maintain segregated client accounts, carry professional indemnity insurance, and have transparent fee structures. Read independent reviews and check complaint databases to understand other traders’ experiences.
What’s the minimum amount needed to start trading with a forex broker?
Minimum deposits vary widely between brokers and account types, ranging from as little as $1 for micro accounts to $10,000 or more for professional accounts. However, having the legal minimum doesn’t mean you should start trading immediately. Most successful traders recommend starting with at least $1,000 to allow for proper risk management and position sizing. Remember that smaller accounts face limitations such as higher relative costs and restricted leverage.
Should I choose a broker based on the tightest spreads available?
While competitive spreads are important, they shouldn’t be your only consideration. Some brokers offer very tight spreads during quiet periods but widen them significantly during news events or volatile conditions. Additionally, brokers with ultra-tight spreads might compromise on execution quality, customer service, or regulatory compliance. Consider total trading costs including commissions, overnight fees, and potential slippage, not just advertised spreads.
Is it safe to use high leverage offered by forex brokers?
Leverage amplifies both profits and losses, making it a double-edged sword. While brokers might offer leverage up to 1000:1, experienced traders typically use much lower levels. High leverage can quickly deplete your account during adverse market movements, even with small price fluctuations. Many regulatory authorities have implemented leverage caps (such as 30:1 in Europe) to protect retail traders. Focus on proper position sizing and risk management rather than maximizing leverage.
How long does it typically take to withdraw money from a forex broker?
Withdrawal processing times depend on your broker’s procedures and chosen payment method. Electronic wallet withdrawals typically process within 24 hours, while bank transfers may take 2-5 business days. Credit card withdrawals often take 3-7 business days due to banking regulations. Regulated brokers usually process withdrawal requests within 1-2 business days, though initial withdrawals might take longer due to additional verification requirements. Be wary of brokers who consistently delay withdrawals beyond their stated timeframes.